You’ll be learning the music intervals : Whole Step and Half Step. A half step (semitone or half tone) is a visual representation of a half step is any two keys on the piano keyboard that have no key in between them.
-
For example,
from key E to key F, or from key B to key C; or
from white key C to black key C# (C sharp),
from white key F to black key F# (F sharp) and so on.
[Review Free Lessons 1 thru 3 below]
HALF STEPS (HS)  A half step is the distance between a black key and a white key that are next to each other on the piano keyboard, for example: (See the above diagram for the examples of half steps) |
|
The distance between C to Db (or C#) is a half step The distance between F to Gb (or F#) is a half step Another example ofthe half steps is the interval between the two white keys, for example: The distance between B and C The distance between E and F |
WHOLE STEPS (WS) 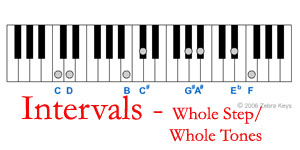 The whole step (whole tone) is an interval of two half steps in between the two keys (notes), for example: (See the above diagram for the examples of whole steps) The distance between C and D is a whole step (with a black key, C#, in between them) The distance between B and C# is a whole step, with a white key, C, in between them The distance between G# to A# is a whole step (with a white key, A, in between them) The distance between Eb to F is also a whole step (with a white key, E, in between them) |
___________________________________
Watch the written version of this tutorial below:
showing you how to play 12 Basic Music Intervals in Flash demos:
Use the keyboard below to play the intervals shown in the video above:
showing you how to play 12 Basic Music Intervals in Flash demos:
Use the keyboard below to play the intervals shown in the video above:
Access free 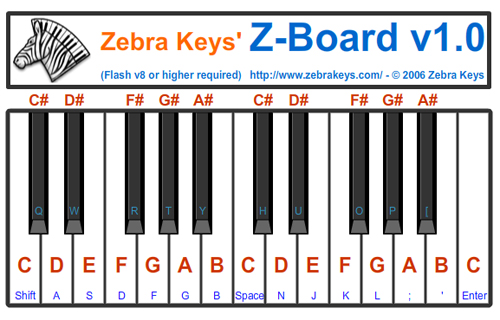 to practice this song now: How to use Z-BOARD For all users (except for those who have a non-touch screen device) – click directly on the keypad of the Z-Board to play that key. |
There are two way to describe Intervals: one is by Interval Number, and the other is by Interval Quality.
1. Interval Number
The interval number is named according to the distance between the two notes of a given interval. These numbers are:
1. Interval Number
The interval number is named according to the distance between the two notes of a given interval. These numbers are:
| U (Unison) | 2nd (Second) |
| 3rd (Third) | 4th (Fourth) |
| 5th (Fifth) | 6th (Sixth) |
| 7th (Seventh) | 8ve (Octave) |
2. Interval Quality
Another way to describe intervals is by quality. Here are the terms used along with their abbreviations in parenthesis.
Another way to describe intervals is by quality. Here are the terms used along with their abbreviations in parenthesis.
|
Perfect (P) Major (M) Minor (m) Augmented (A) Diminished (d) |
___________________________________
[Note:
WS – Whole Step
HS – Half Step
Unison, Fourth, Fifth, Octave
These intervals may be perfect (P), augmented (A), or diminished (d).
A perfect unison occurs between notes of the same pitch, so it is zero (0) half step. A perfect fourth is five half steps. A perfect fifth is seven half steps. A perfect octave is twelve half steps. In each case, an augmented interval contains one (1) half step more, and a diminished interval contains one (1) half step less.
WS – Whole Step
HS – Half Step
Unison, Fourth, Fifth, Octave
These intervals may be perfect (P), augmented (A), or diminished (d).
A perfect unison occurs between notes of the same pitch, so it is zero (0) half step. A perfect fourth is five half steps. A perfect fifth is seven half steps. A perfect octave is twelve half steps. In each case, an augmented interval contains one (1) half step more, and a diminished interval contains one (1) half step less.
|
• Perfect Unisons are zero half step (HS) • Perfect Fourths are five half steps (HS) • Perfect Fifths are seven half steps (HS) • Perfect Octaves are twelve half steps (HS) |
Second, Third, Sixth, Seventh
These intervals may be major (M), minor (m), augmented (A), or diminished (d).
These intervals may be major (M), minor (m), augmented (A), or diminished (d).
|
• Major seconds are two HS (or one WS); minor seconds are one HS • Major thirds are four HS (or two whole steps); minor thirds are three HS • Major sixths are nine HS; minor sixths are eight HS • Major sevenths are eleven HS; minor sevenths are ten HS |
___________________________________
In each case, the augmented interval contains one (1) half step more than the major interval, and the diminished interval contains one (1) half step fewer than the minor interval.
| ___________________________________ |
| You May Also Like: |
| Access free Virtual Piano | List of 50 Free Piano Lessons | Free Interactive Interval Ear Trainer |
How to play C Major Scale Learn the Names of White Keys:  Learn the Names of Black Keys: 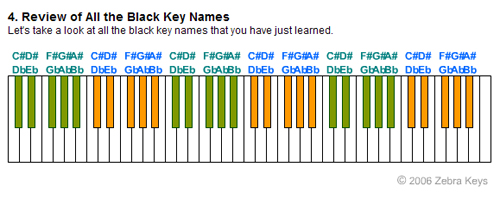 Lesson 4 – Piano Grand Staff Lesson 5 – Music Notation – Note Durations Beginner Piano Lesson 6 – Learn Song, Brother John Lesson 9 – Playing the Major Chord Lesson 10 – Three Primary Chords Lesson 11 – 12 Bar Blues Chord Progression Lesson 12 – 12 Keys of Music Lesson 13 – Major Scale Lesson 14 – Intervals Lesson 15 – Chords of the Major Scale Lesson 16 – Circle of Fifths |
| ____________________________ |
| Click below to access: |
| Page 1 | | | Page 2 | | | Page 3 | | | Page 4 | | | Page 5 |
| Page 6 | | | Page 7 | | | Page 8 | | | Page 9 | | | Page 10 |
| Page 11 | | | Page 12 | | | Page 13 | | | Page 14 | | | Page 15 |
|
Lesson 2 White Key Names  |
Lesson 1 Piano Layout  |
Lesson 3 Black Keys Names  |
Free  |
Piano  |
Tutorials  |
Lesson 4  |
Lesson 5  |
Lesson 6  |
Learn for Free – Online Piano Lessons
| 1 | | | 2 | | | 3 | | | 4 | | | 5 | | | 6 |
| 7 | | | 8 | | | 9 | | | 10 | | | 11 | | | 12 |
| 13 | | | 14 | | | 15 | | | 16 | | | 17 | | | 18 |
| 19 | | | 20 | | | 21 | | | 22 | | | 23 | | | 24 thru 50 |
Fun-Learning with Free Games  |
|
|

